ROS 2
Load local and remote MCAP files containing ROS 2 data, or connect directly to a live ROS 2 stack.
Live data
Install ROS 2, and make sure you are on the same network as the robot.
In Foxglove, select "Open connection" in the "Open data source" dialog.
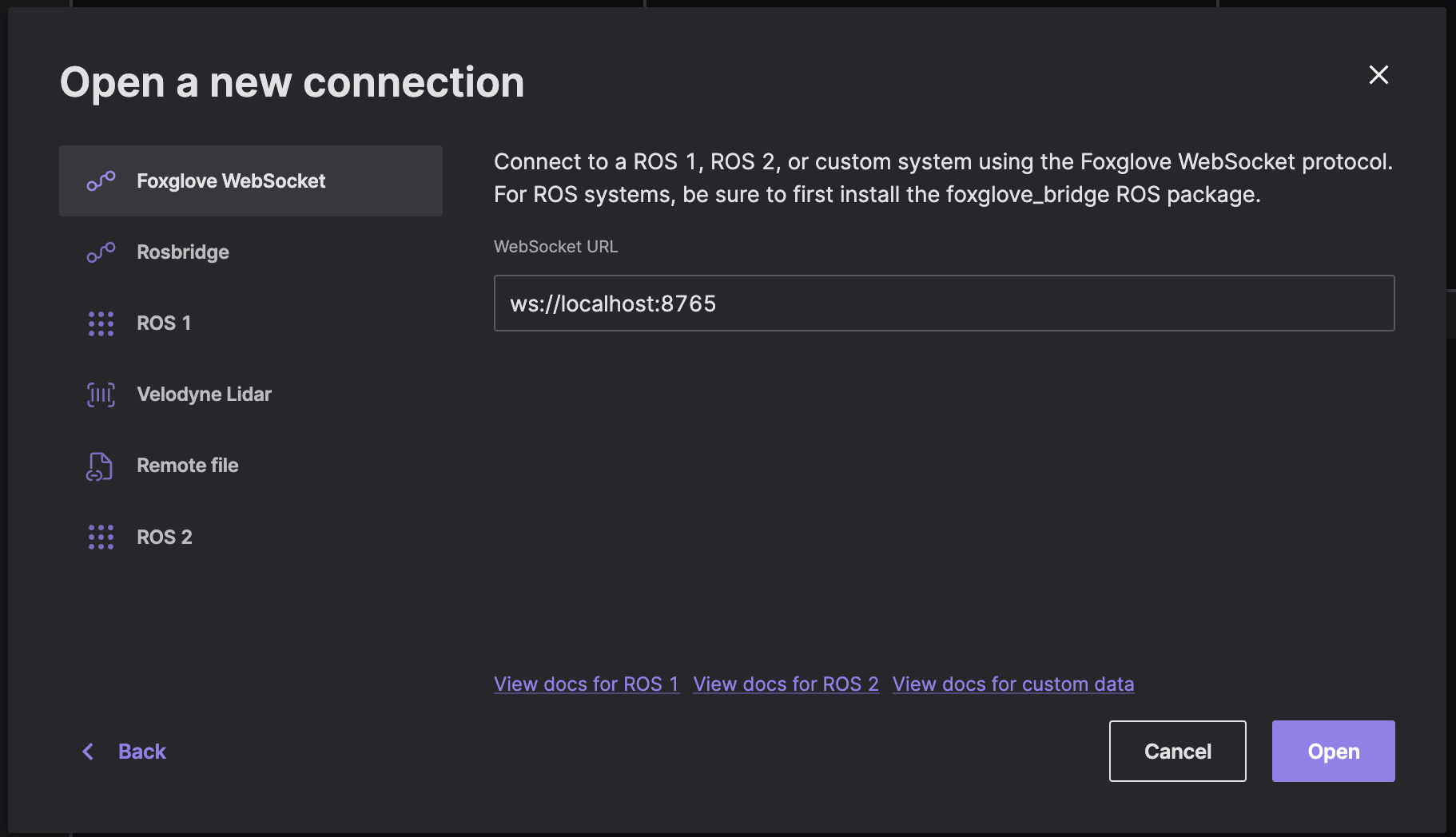
Foxglove WebSocket
We recommend Foxglove WebSocket as the easiest way to get connected – especially if you have a network firewall between ROS and Foxglove, as it requires your ROS host to have only one port open.
This option requires running an extra ROS node (foxglove_bridge) – follow the installation directions here.
Connect
Select "Foxglove WebSocket" in the "Open data source" dialog, then enter the URL to your Foxglove bridge server:
Reset connection
To reconnect to a Foxglove WebSocket in a different context, you must first clear out your most recently visualized data in Foxglove.
To clear the state and reset your visualizations, resend the serverInfo message with an updated value for its optional sessionID field (string value). This lets the Foxglove WebSocket connection know that you are initiating a new connection, instead of trying to reconnect to a dropped one.
Limitations
Foxglove WebSocket connections support publishing back to your ROS stack, as well as reading and setting ROS parameters.
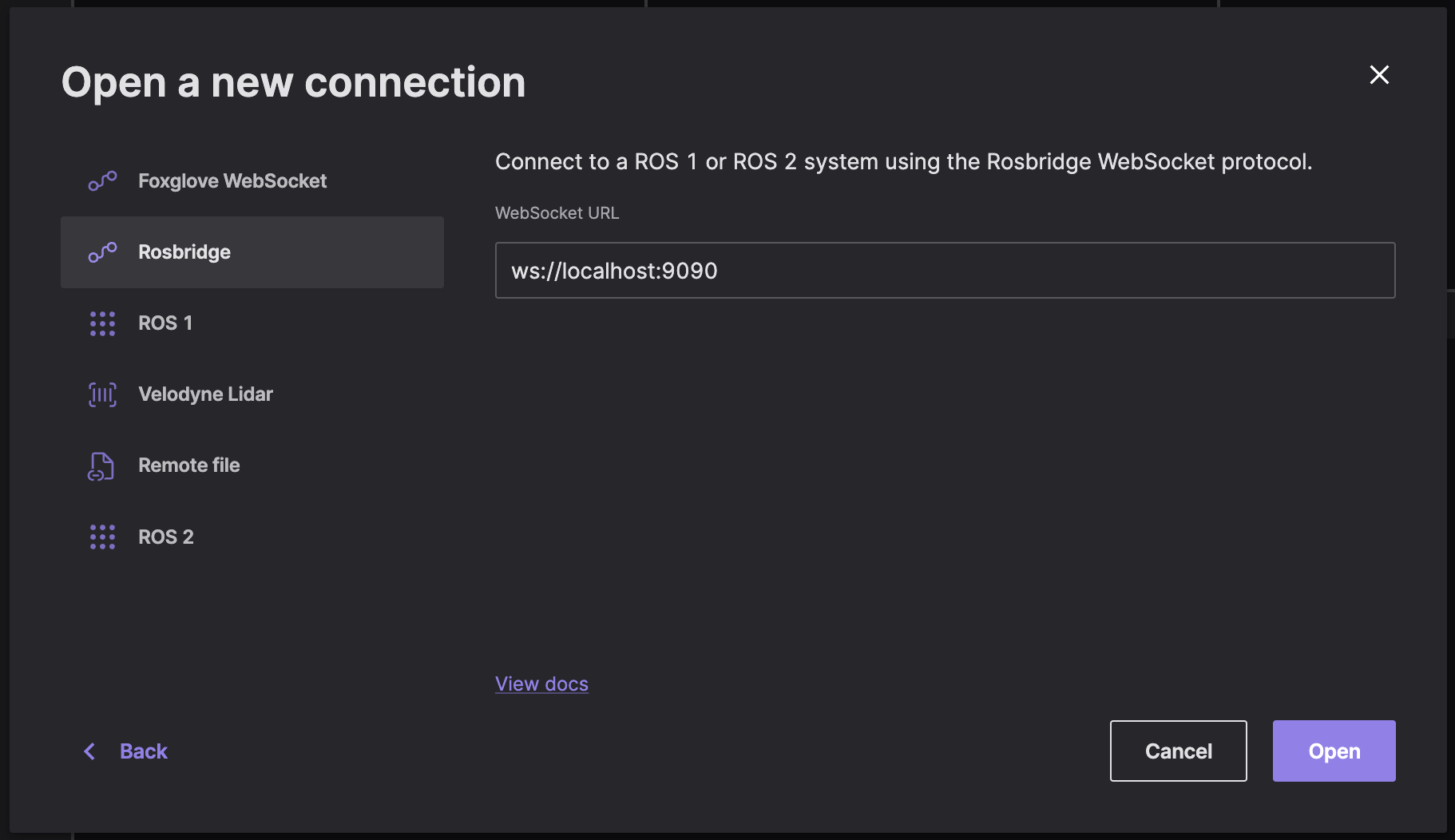
Rosbridge
NOTE: For performance reasons, we recommend using the Foxglove WebSocket connection instead.
Connect directly to your running ROS stack via WebSockets using a Rosbridge connection. This connection option requires only a single open port between Foxglove and your robot.
A rosbridge connection uses a standard protocol to connect Foxglove to your ROS master over WebSockets. While it does require running an extra ROS noderosbridge_server, we recommend this option if you have a network firewall between ROS and Foxglove, as it requires your ROS host to have only one port open.
To open a Rosbridge connection, make sure you’ve installedrosbridge-suite
$ sudo apt install ros-galactic-rosbridge-suite // ROS 2 Galactic
Next, start the WebSocket server, and review the command printout to determine the port it is listening on (e.g. ws://0.0.0.0:9090):
$ ros2 launch rosbridge_server rosbridge_websocket_launch.xml
"Open connection" in the "Open data source" dialog, select "Rosbridge", then enter the URL to your Rosbridge server:
To test your connection, open the sidebar to verify that Foxglove is receiving your data source's topics.
Limitations
Rosbridge connections support publishing back to your ROS stack, but not reading or setting ROS parameters.
Remote file
Remote ROS 2 .db3 files are not supported, but you can convert them into MCAP files for remote file support.
Select "Remote file" in the "Open data source" dialog, and enter the URL to your remote .mcap file.
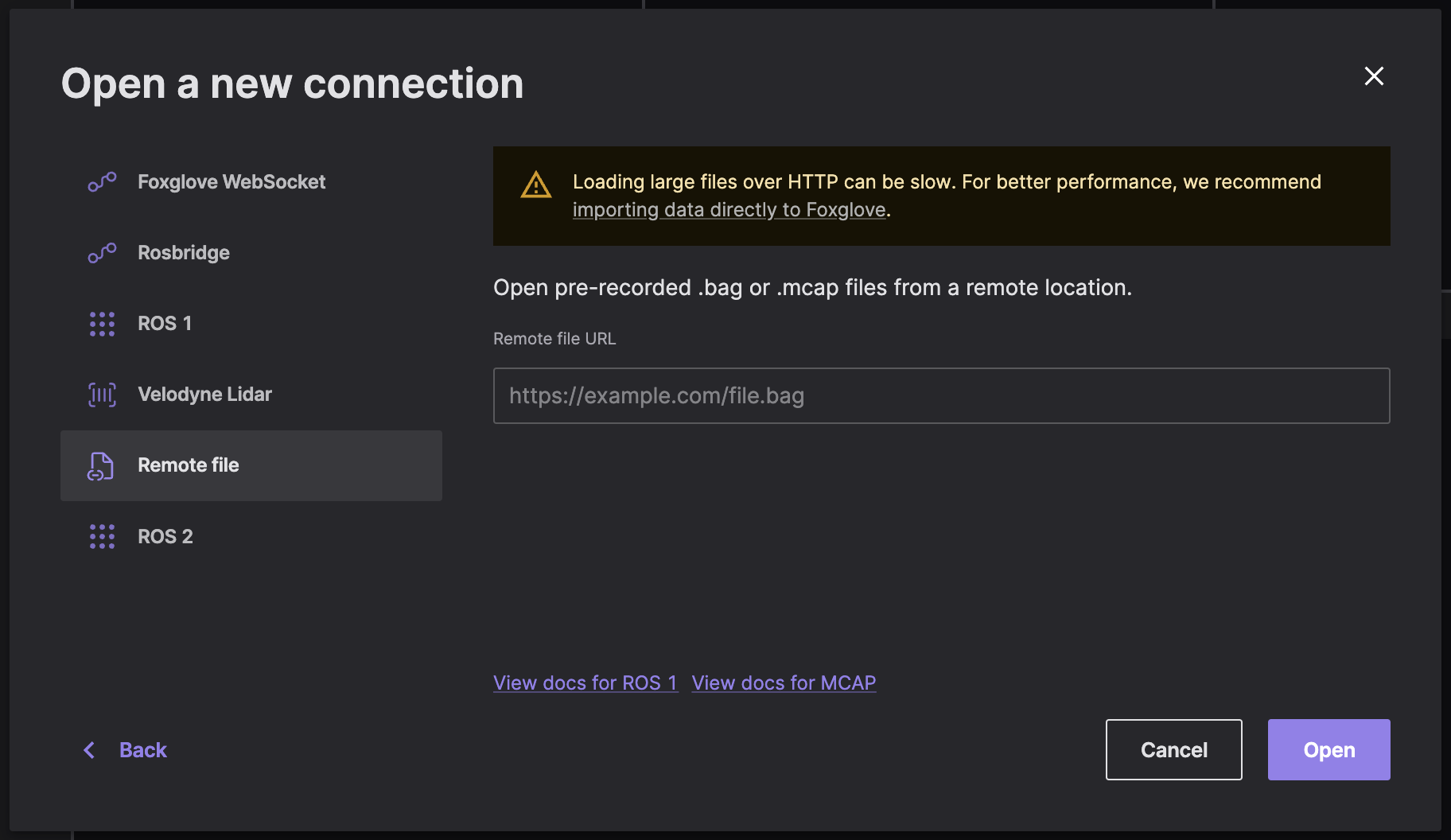
Check out the directions for setting up CORS to load remote data files into Foxglove.
Local data
You must first convert ROS 2 (.db3) files into the supported MCAP file format before loading in Foxglove.
Use the mcap CLI tool to help with this conversion:
$ mcap convert ros2_input.db3 ros2_output.mcap
mcap will search the path stored in your $AMENT_PREFIX_PATH environment variable to locate the ROS message definitions on your hard drive. You can also specify a colon-separated list of directories for the CLI tool to search using the ament-prefix-path flag:
$ mcap convert ros2_input.db3 ros2_output.mcap --ament-prefix-path=/your/first/directory;/your/second/directory
Once you have your MCAP (.mcap) file, you're ready to load it for visualization.
To load a local file for visualization, you have several options:
- Double-click the file from your file manager
- Drag-and-drop the file into Foxglove directly
- "Open local file" in the "Open data source" dialog to select a file from your filesystem
Imported data
First convert your ROS 2 files to MCAP.
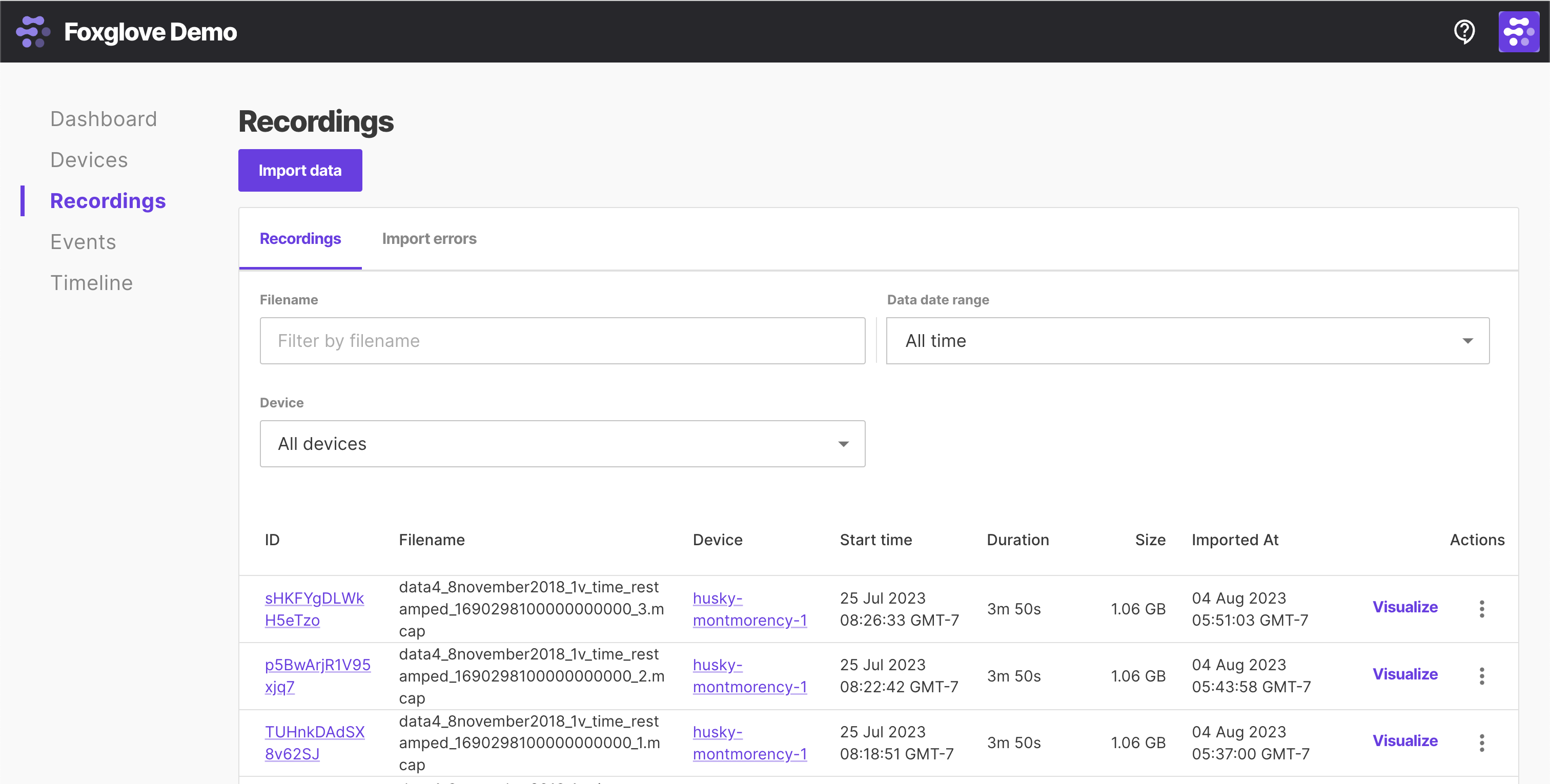
After importing data to Foxglove, select individual resources to "Visualize" on the Recordings or Events pages:
Select a custom time range of data (can span multiple recordings or events) to "Visualize" on the Timeline page: